Keyword research training from zero to one hundred

Keyword research is a fundamental part of SEO. In Chapter 2, we covered how to submit your site to Google (the search engines), and in this chapter, you’ll learn how to find your niche and how to find profitable keywords that you can rank for.
| Guide to this article (click on the articles you are looking for to jump to the article you are looking for!) |
Keyword research should be the first step on your SEO journey. It’s especially important in two common scenarios:
- Know your niche: When launching a new website, keyword research can provide an overview of the niche and main topics for people in your niche or industry.
- Find new content ideas: Keyword research can help you find the most profitable keyword opportunities and plan your content strategy.
Where to find keywords?
There are many ways to find keywords. Your first task is to find primary keywords, phrases that you use as stepping stones to find more keyword ideas. If you’re starting a coffee blog, simple phrases like “coffee beans,” “coffee machines,” or “espresso” will work great.
Classic methods for keyword research:
Google suggestions
Google offers many keyword suggestions directly in the SERP. The SERP is what you type into the browser bar and then it gives you various suggestions!Features like Google autocomplete, query completion, or related searches can be a great source of keyword ideas. With autocomplete, you just type your main or core keyword into Google search and suggestions will appear automatically.
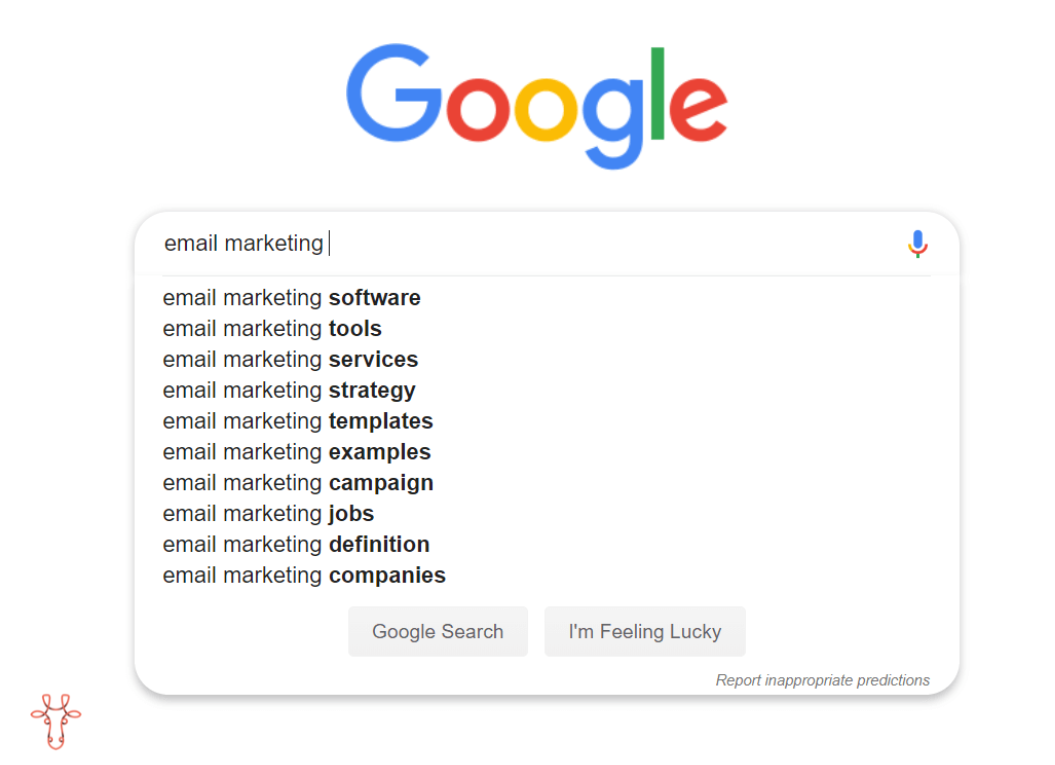
Google’s autocomplete feature
You can combine your primary keyword with different letters of the alphabet to find more autocomplete ideas (e.g. keyword B, keyword T, keyword M, …). Here’s another example of keyword ideas you can find on the Google results page:
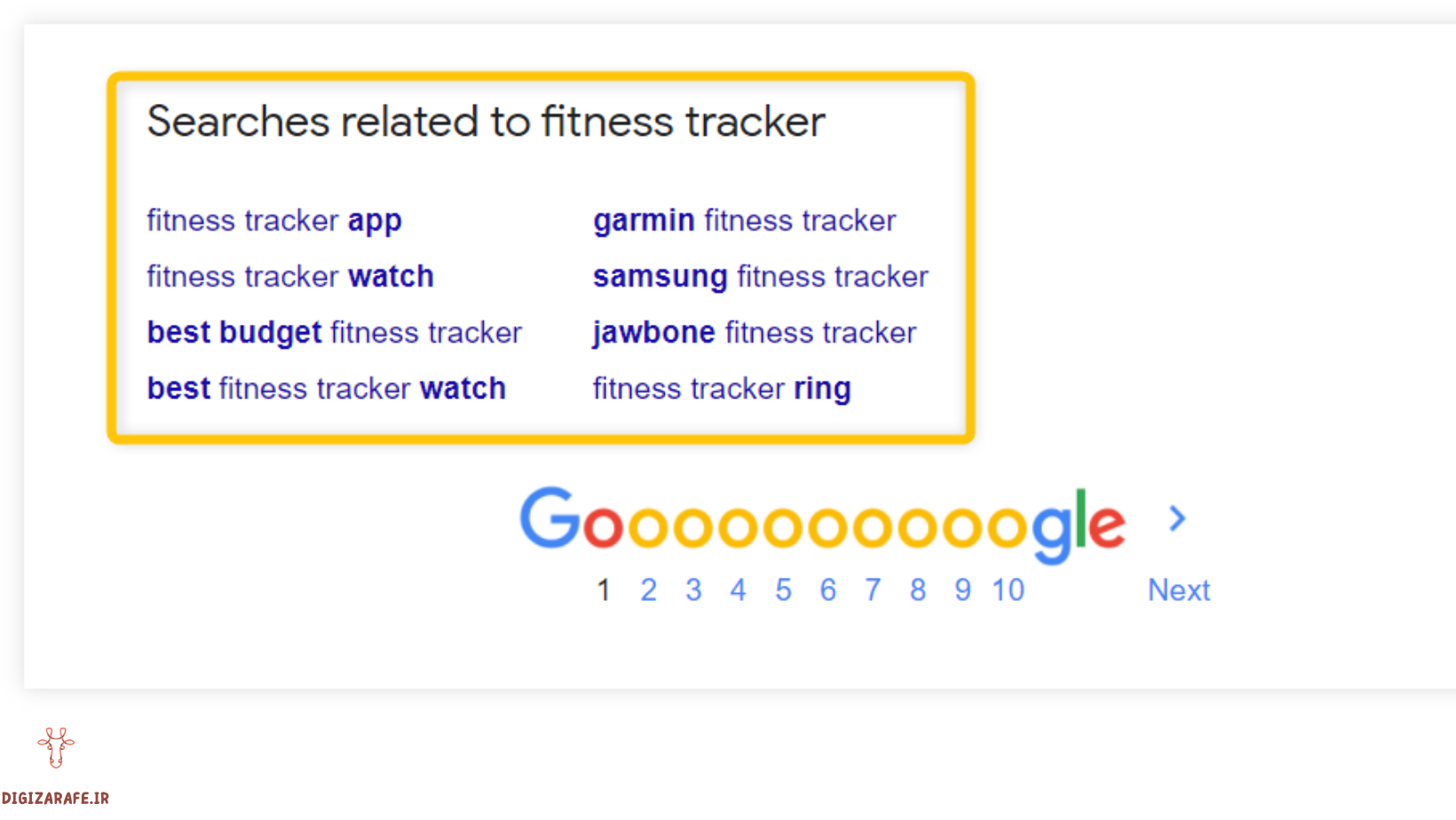
Google Similar Results Feature: Perfect for Keyword Selection
Google’s suggestions are based on real searches used by people around the world.
Note: There are many other platforms besides Google that can help you find new keyword ideas. Focus on those that people in your niche use to ask questions, connect, and share ideas.As an example of Digi Giraffe Eye: Reddit, YouTube, site forums, Facebook groups, Pinterest, and popular and service-providing sites are Digital Giraffe’s suggestions.
Keyword tool
There are many free keyword tools that can give you hundreds of keyword ideas based on a single, central keyword. The problem is: they are very limited when it comes to other features. So if you are making money with your website in any way, a quality paid keyword tool is a great investment that will pay off sooner or later.
In addition to keyword suggestions, professional tools provide other useful SEO metrics and insights to evaluate keywords and choose the best ones. So they can save you time and give you a competitive advantage. There are two ways to start keyword research with keyword tools:
- Main keyword (your core keyword)
- Competitor domain/URL
In addition to keyword suggestions, keyword tools calculate keyword ranking difficulty and help you analyze SERPs. All of this brings us to the next important part:
Keyword criteria
Your goal is to find relevant keywords with high search volume and low keyword difficulty, an ideal combination of the three important factors of keyword research.

3 important factors in choosing keywords
We call this principle the Keyword Tripod Rule, and the three factors represent the tripod. As soon as one of the legs is taken, the tripod collapses.
Search volume
In the past, content creators would only do keyword research to find keywords with high search volume. They would stuff keywords into content to trick search engine algorithms and ensure high rankings in organic search. Since then, keyword research has become much more sophisticated.
Long-tail keywords vs. search volumeFirst of all, let me say that the Persianized Long Tail Keywords are long keyword, long keyword, long-tail keyword, and multi-word keyword. Many keyword research guides recommend focusing on so-called long tail keywords, keywords that are more specific and usually consist of more words. The reason is simple: Long tail keywords usually have lower difficulty and higher conversion rates. This is because the query is more specific, so there is a higher chance that a user will click on your long tail keywords. Results show that about 70% of all traffic comes from long tail keywords. 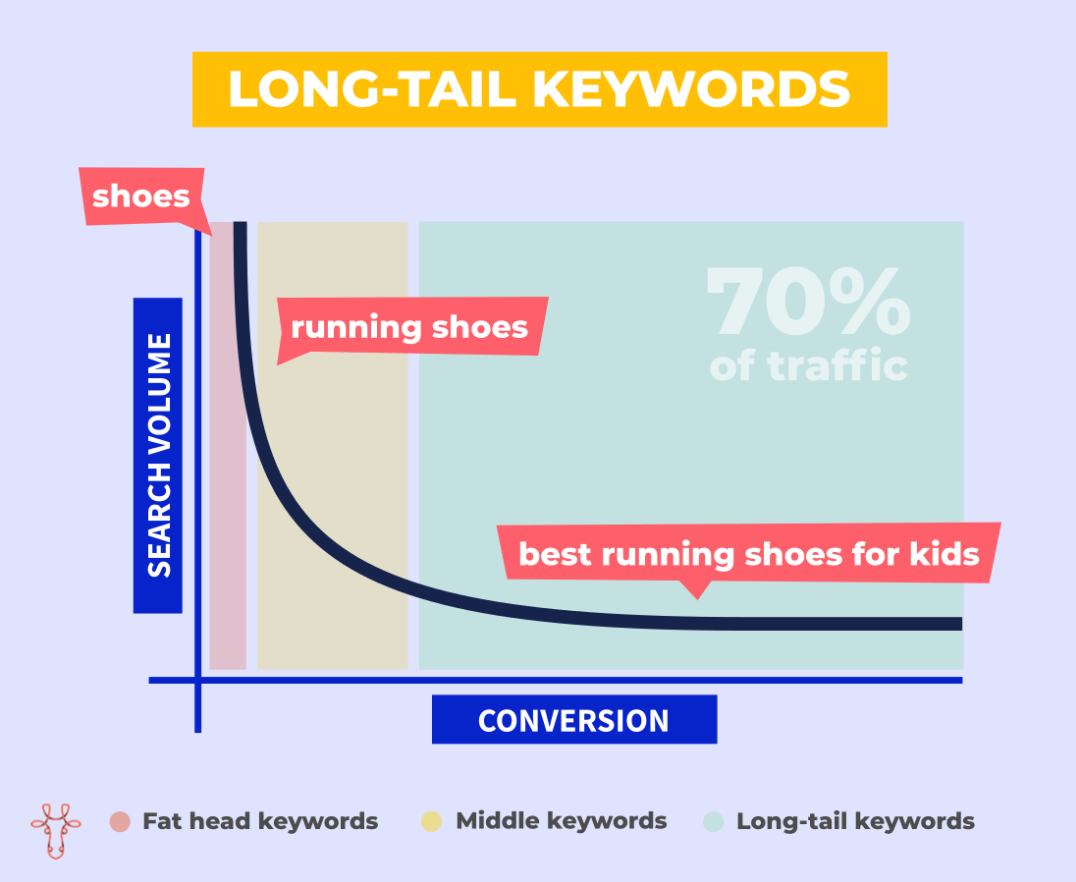 Multi-word keywords, long-tail keywords, or long-tail keywords Of course, the downside is lower search volume, so you need to consider all aspects and find a balance between the effort and the potential benefits. |
Additionally, ranking only for high-volume keywords is not always possible. The truth is, as a new website, you simply can’t rank for big keywords. This doesn’t mean you shouldn’t try it once you’ve established yourself in the market and gained some traction. It’s all about assessing your real chances. A metric called keyword difficulty can help you with this.
Keyword difficulty
Once you have found the keywords you want to rank for, you need to do a competitive analysis to see how strong and difficult they are. This is usually expressed in a metric called keyword difficulty. In most tools, the keyword difficulty value is shown on a scale from 0 to 100. The higher the keyword difficulty number, the more difficult it is for the keyword to rank in SERP 1. This is based on the ranking authority of the pages for the given keyword.
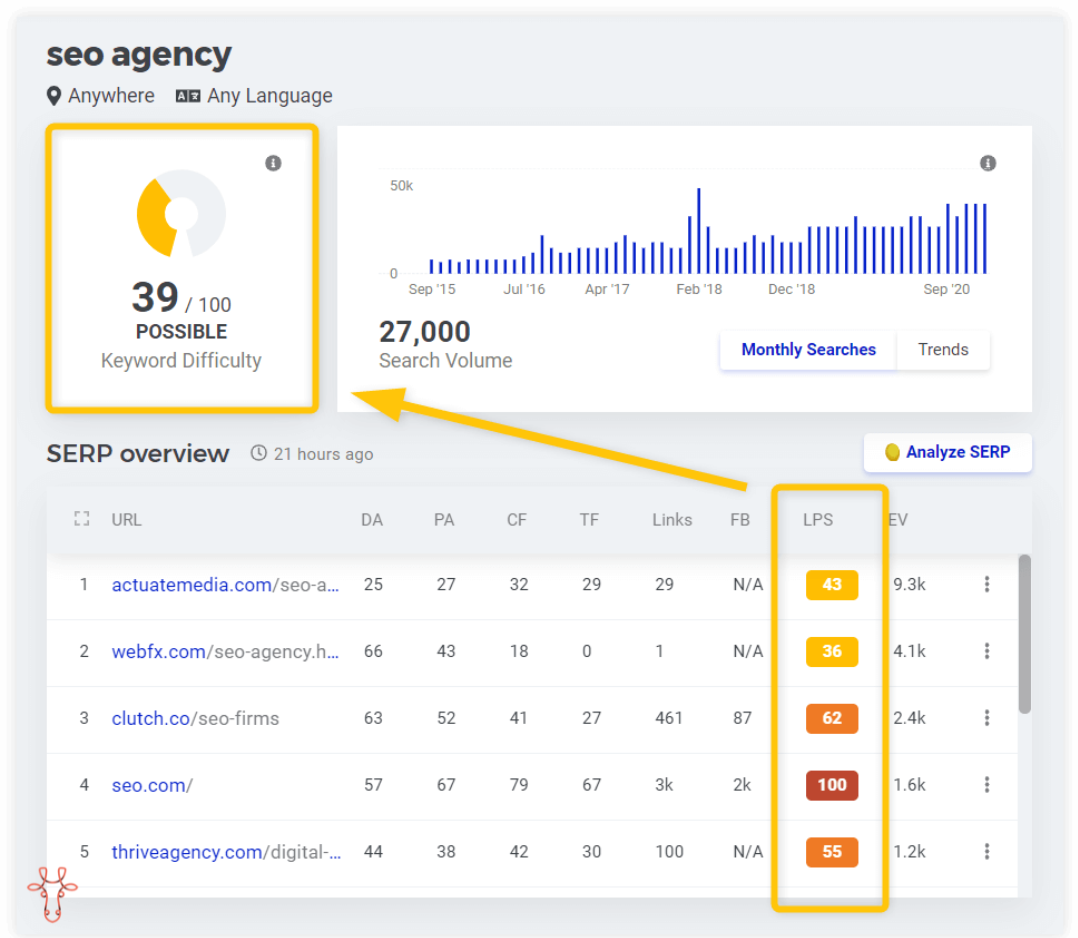
Checking keyword difficulty in keyword search tools
According to keyword difficulty:
- You get an overview of the “big” keywords and “big” competitors in your niche.
- You will be able to identify keywords that you have a better chance of ranking for.
- You can save a lot of time by focusing on keywords that can bring you results, even if you don’t have much power yet.
| Note: Keyword difficulty values may vary across tools, you may see a score of 30 in one tool and 50 in another for the exact same keyword. This is because the calculations are based on slightly different metrics and algorithms. The important thing is to compare results across tools. |
Keyword relevance
Lastly, your keyword needs to be relevant. The easiest way is to do a proper analysis to find out the following:
- Whether you can compete with websites ranked number one on the SERP. (See the previous section on keyword difficulty)
- What is the search intent behind the keywords you want to optimize for?
By looking at the SERP, you can determine what the search intent behind the query is and whether it matches your content. This is a very, very important issue that the DigiZiraffe team has prepared. There are 4 different types of search intent:
- Navigation: Search for a specific website/brand.
- Informational: Searching for public information and raising awareness.
- Transactional: The user wants to buy something online.
- Commercial: The user does research before purchasing.
Look at this table for some examples:
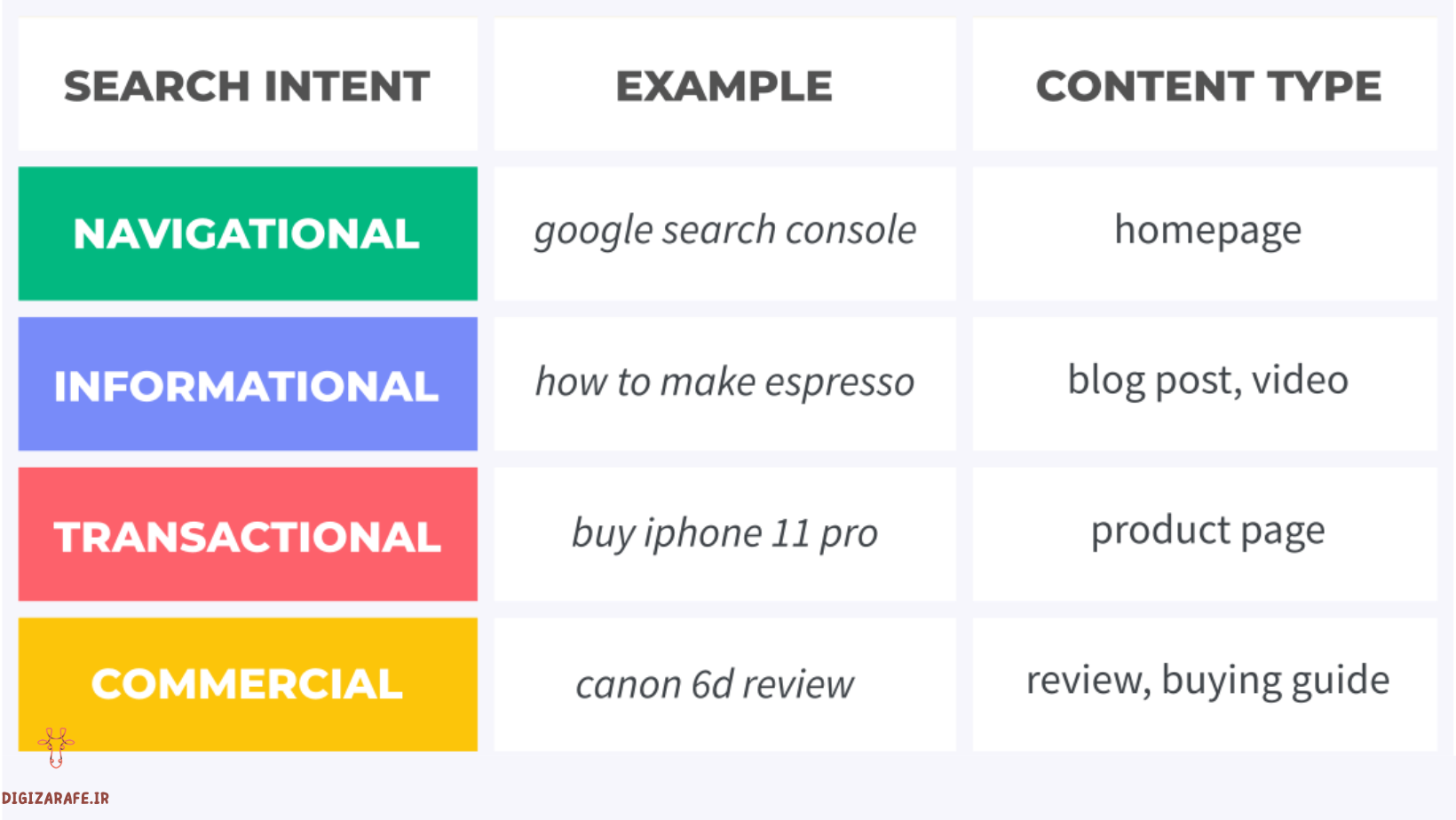
4 main examples of people’s search goals on search engines
Let’s say you have an e-commerce store selling fitness equipment. You want to optimize your squat rack product page and you find the keyword “best squat rack.”It has good search volume and isn’t too difficult. However, if you look at the search results, you’ll notice that all of the pages ranking for “best scott’s rack” are reviews and buying guides, not product pages. In other words, Google sees it as a business keyword, not a transactional one.
A quick look at the SERP will tell you this.
Always keep this in mind so you don’t end up optimizing for the wrong keywords.
Expert insights on keywords from Gael Burton, SEO expert and founder of Authority HackerOne of the biggest mistakes people make in keyword research is that they only look at the numbers they see in the keyword tool. They rarely consider search intent, when in reality, it’s even more important than search volume. why? First, Google really knows what kind of content it wants to see for each query and search, and if you check the top results, you’ll often see similar results. So if you’re not in the categories they want to see, your chances of ranking are very slim, even if you meet all the link criteria. Secondly, even if you do get visitors from Google, small changes in the query mean very different things to people, and some may be interested in buying your stuff while others don’t really care. For example: If you look at the keyword “vacuum cleaner,” a lot of people are searching for it (223,000 average monthly search volume). But people are mostly looking for brand results and e-commerce pages, which is why Google returns results for Amazon, Dyson, and Walmart, and you’re probably not selling anything to them. 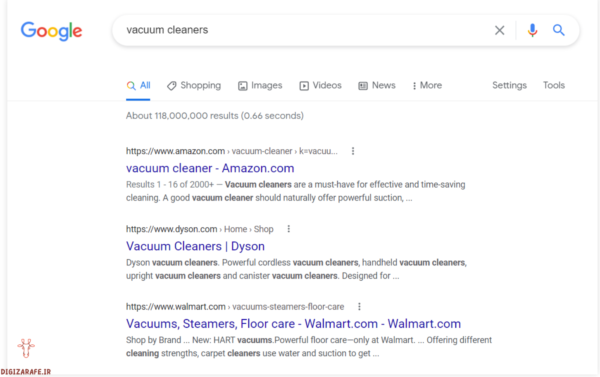 Priority is given to purchasing products from reputable brands. While the phrase “best vacuum cleaner” has a much lower search volume (average 13,000 monthly search volume), this query is more commercial in nature and will certainly generate more revenue, which is why Google shows a shopping guide instead of a Walmart product page. 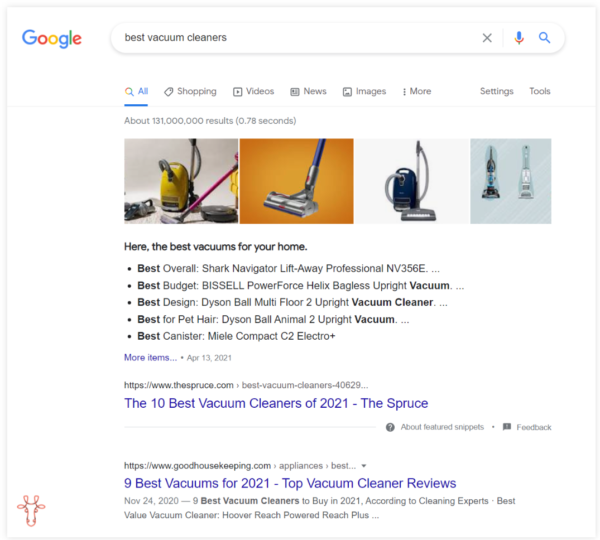 Google Smart Search and Handwriting So don’t just focus on search volume, intent is the most important metric. |




